This post shows a Java program to multiply two matrices.
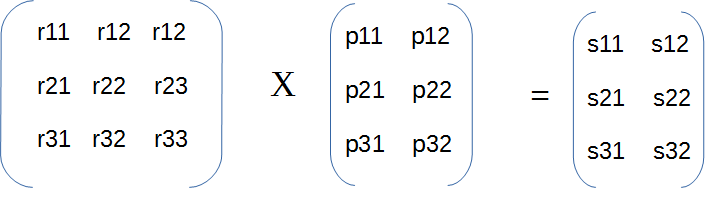
To multiply one matrix with another you need to do a dot product of rows and columns. Let’s see it with an example where you are trying to multiply a 3X3 matrix with a 3X2 matrix.
How matrix multiplication happens here using dot product can be explained as follows-
First row of first matrix is multiplied with the first column of second matrix.
s11 = r11Xp11 + r12Xp21 + r13Xp31
Second row of first matrix is multiplied with the second column of second matrix.
s12 = r11Xp12 + r12Xp22 + r13Xp32
Then second row of first matrix is multiplied with the first column of second matrix.
s21 = r21Xp11 + r22Xp21 + r23Xp31
and so on...
Java program for matrix multiplication
In the matrix multiplication Java program, initially user is prompted to enter the matrices. You can also check that the number of columns in the first matrix are equal to the number of rows in the second matrix. Then using these two matrices you can do the multiplication.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MatrixMultiplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter number of rows and columns in the matrix : ");
int r1 = in.nextInt();
int c1 = in.nextInt();
// First matrix
int[][] matrix1 = prepareMatrix(r1, c1);
System.out.print("Enter number of rows and columns in the matrix : ");
int r2 = in.nextInt();
int c2 = in.nextInt();
if(c1 != r2){
in.close();
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number of columns in the first matrix should be equal to the number of rows in the second matrix");
}
// Second matrix
int[][] matrix2 = prepareMatrix(r2, c2);
// multiplied result stored in this matrix
int multiplyMatrix[][] = new int[r1][c2];
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < r1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < c2; j++){
for(int k = 0; k < c1; k++){
sum = sum + matrix1[i][k] * matrix2[k][j];
}
multiplyMatrix[i][j] = sum;
sum = 0;
}
}
System.out.println("Multiplied Matrix : " );
for(int i = 0; i < r1; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < c2; j++){
System.out.print(" " +multiplyMatrix[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
if(in != null){
in.close();
}
}
private static int[][] prepareMatrix(int row, int column){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter elements of Matrix : ");
int matrix[][] = new int[row][column];
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < column; j++){
matrix[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println("Entered Matrix : " );
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < column; j++){
System.out.print(" " +matrix[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
return matrix;
}
}
Output
Enter number of rows and columns in the matrix : 3 3 Enter elements of Matrix : 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 Entered Matrix : 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 Enter number of rows and columns in the matrix : 3 3 Enter elements of Matrix : 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Entered Matrix : 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Multiplied Matrix : 96 114 132 240 294 348 384 474 564
That's all for the topic Matrix Multiplication Java Program. If something is missing or you have something to share about the topic please write a comment.
You may also like
- Matrix Addition Java Program
- Matrix Subtraction Java Program
- How to Get The Last Modified Date of a File in Java
- Generic Bubble Sort Java Program
- Difference Between sleep() And wait() Methods in Java
- Exception Handling With Method Overriding in Java
- Java Immutable Set With Examples
- Injecting Prototype Bean into a Singleton Bean in Spring